By 2030, Non-Communicable Diseases are expected to surpass infectious, maternal, and child diseases as the leading cause of death, even in Sub-Saharan Africa. Understanding free radicals is crucial in combating this trend!
Lusaka, Aug. 4 – By Mpandashalo Mwewa.
TOPLINE: You’ve likely encountered the term “free radicals,” often mentioned alongside “antioxidants.” Free radicals present a universal challenge, while antioxidants offer the solution. This is why the study of Vitamin E, one of the most potent antioxidants, is gaining attention.
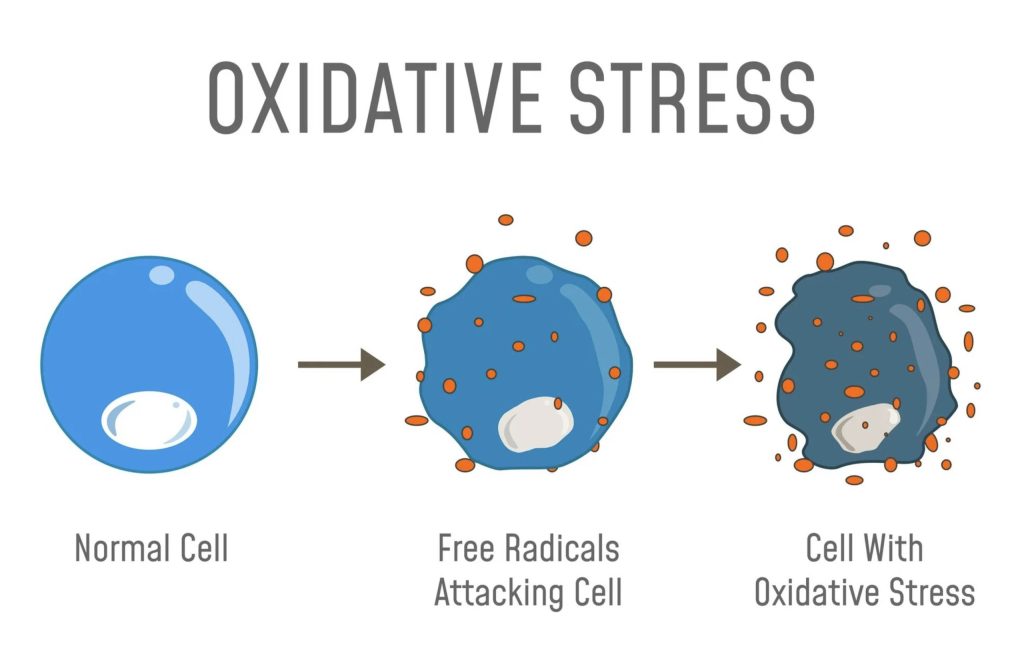
Free radicals form when our bodies break down molecules into individual atoms, leading to some atoms becoming unstable. For instance, water (H2O) breaks down into two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Normally, a stable oxygen atom has eight electrons. However, if an oxygen atom ends up with only seven electrons after this breakdown, it becomes unstable.
Unstable atoms, or free radicals, seek stability by aggressively pairing with other elements to acquire the missing electron. This activity causes oxidative stress within the body.
Oxidative stress is linked to aging and various non-communicable diseases (NCDs), such as cardiovascular diseases, cancers, chronic respiratory diseases, and diabetes. NCDs disproportionately impact low- and middle-income countries, accounting for over three-quarters of global NCD deaths, amounting to 31.4 million annually.
KEY POINTS
◾By 2030, NCDs are expected to surpass infectious, maternal, and child diseases as the leading cause of death, even in Sub-Saharan Africa. Understanding free radicals is crucial in combating this trend!
◾NCDs, also known as chronic diseases, tend to be of long duration and are the result of a combination of genetic, physiological, environmental and behavioural factors. The main types of NCDs are cardiovascular diseases (such as heart attacks and stroke), cancers, chronic respiratory diseases (such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma) and diabetes.
◾Cardiovascular diseases account for most NCD deaths, or 17.9 million people annually, followed by cancers (9.3 million), chronic respiratory diseases (4.1 million), and diabetes (2.0 million including kidney disease deaths caused by diabetes). These four groups of diseases account for over 80% of all premature NCDs deaths. And of all NCDs deaths, 77% are in low – and middle – income countries.
◾Exposure to tobacco smoke, physical inactivity, the harmful use of alcohol, unhealthy highly processed foods and air pollution all increase the risk of dying from NCDs.
◾CRUCIAL QUOTE
“By 2030, Non-Communicable Diseases are expected to surpass infectious, maternal, and child diseases as the leading cause of death, even in Sub-Saharan Africa!” – Dr. Chitalu Chilufya, a public health physician and former Minister of Health who led the radical transformation of the Zambia national health system in pursuit of Universal Health Coverage.
◾MAJOR SOURCES OF FREE RADICALS
▪️Normal Metabolic Processes: The body’s regular metabolic activities, especially cellular respiration in mitochondria, generate free radicals as byproducts. During the conversion of oxygen into energy, a small percentage of oxygen molecules become free radicals.
▪️Environmental Exposures: Pollution, radiation, cigarette smoke, and industrial chemicals introduce free radicals into the body. These external sources significantly increase oxidative stress and the potential for cellular damage.
▪️Inflammation: The immune system produces free radicals to combat infections and heal injuries. While this is a natural defense mechanism, chronic inflammation can result in excessive free radical production, leading to tissue damage.
▪️Exercise: Physical activity, particularly intense or prolonged exercise, increases oxygen consumption. This heightened oxygen use can lead to a higher production of free radicals.
▪️Diet: Consuming foods high in fats and sugars can elevate free radical formation. Additionally, contaminants and additives in processed foods can introduce free radicals.
▪️Alcohol and Drugs: Excessive alcohol intake and certain medications can enhance free radical production, contributing to liver damage and other health issues.
▪️UV Radiation: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun can induce the formation of free radicals in the skin, leading to skin damage and increasing the risk of skin cancer.
◾MITIGATING FREE RADICAL ACCUMULATION
▪️Antioxidant-Rich Diet: Consuming foods high in antioxidants, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, helps neutralize free radicals. Antioxidants like vitamins C and E, selenium, and flavonoids are particularly effective.
▪️Regular Exercise: Engaging in moderate, regular physical activity boosts the body’s antioxidant defenses, despite the initial increase in free radicals during exercise.
▪️Avoiding Environmental Toxins: Limiting exposure to pollutants, cigarette smoke, and industrial chemicals reduces the external sources of free radicals.
▪️Sun Protection: Using sunscreen and wearing protective clothing can shield the skin from harmful UV radiation.
▪️Limiting Alcohol and Drugs: Reducing alcohol consumption and using medications responsibly can decrease free radical production.
◾KEY BACKGROUND
Zambia faces one of the highest cancer incidence rates in Africa, particularly affecting individuals aged 25 to 45, much younger than in developed nations. For years, the Zambian Government prioritized combating cancer, with the 2007 inauguration of the country’s first Cancer Disease Hospital (CDH) marking a significant milestone. However, the CDH has since deteriorated, underscoring the urgent need for Zambians to focus on cancer prevention.
Understanding the sources of free radicals and implementing counteractive measures is essential in mitigating their harmful effects, thereby promoting health and longevity. As non-communicable diseases (NCDs) surpass infectious diseases in global mortality rates, it is projected that by 2030, NCDs will claim more lives than infectious, maternal, and child diseases combined, even in Sub-Saharan Africa.
◾FURTHER READING
▪️Why cancer is rising among young adults | Link
▪️Dr. Chilufya Discusses the Best Teas Rich in Antioxidants for This Flu-Infested Season | Link
▪️Eating pineapples regularly can prevent NCDs – Dr. Chilufya | Link
About Our Advocacy: Woodpecker’s Digest, an online platform, provides analyses and commentaries on pertinent issues of national interest, complemented by articles focusing on personal development and health. Journalism is a powerful tool for driving positive socio-economic change!
©2024 Woodpecker’s Digest.
Putting news into perspective








